Lead glass at airports — radiation protection and safety

Lead glass is a material of critical importance in protection against ionizing radiation. At airports, where baggage and passenger screening is conducted using X-ray scanners, the use of appropriate protective materials is essential. Lead glass provides an effective protective barrier against radiation, which can be harmful to health, especially with prolonged exposure. This article discusses why lead glass is an indispensable element in airport infrastructure, how it enhances the safety of both employees and passengers, and the technical innovations associated with this material used in such facilities.
Lead glass is a material that performs exceptionally well under the most demanding conditions, including areas where X-ray radiation is emitted. Radiation protection at airports is not just about compliance with standards but also about ensuring maximum safety for everyone in zones exposed to radiation.
Why is lead glass so important at airports?
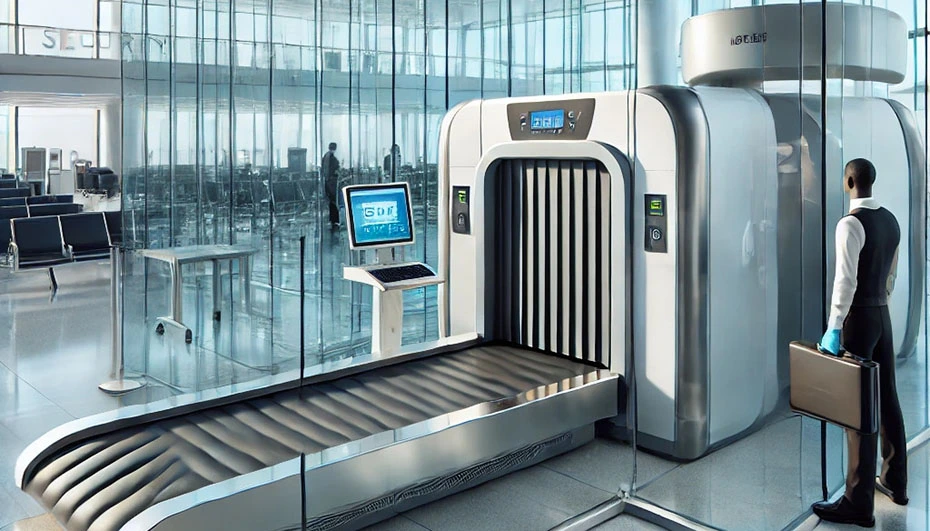
At airports, where baggage and passenger screening is conducted using X-ray radiation, the use of lead glass is crucial to ensure the protection of personnel operating the X-ray scanners as well as passengers who may be exposed to radiation.
Protection against X-ray radiation
Lead glass effectively absorbs X-ray radiation, making it an ideal protective material in areas where radiation is used for control purposes. At airports, lead protective windows in screening zones ensure that scanner operators can safely work while monitoring passenger baggage without being exposed to harmful radiation. Lead glass is particularly valuable in control rooms, where prolonged exposure to X-ray devices could lead to serious health risks.
Lead glass is a material that blocks harmful radiation while maintaining full transparency. This allows operators to fully observe the baggage scanning process and conduct real-time verification without exposing themselves to radiation.
Technical facts about lead glass at airports
- Different thicknesses of lead glass depending on radiation levels
The thickness of lead glass at airports varies depending on the intensity of X-ray radiation in specific areas. In zones where radiation levels are particularly high—such as baggage scanning areas—thicker lead glass is used. In less exposed areas, thinner lead glass panels are sufficient to effectively block radiation while maintaining protection.
- Resistance to high temperatures
Lead glass demonstrates exceptional resistance to high temperatures, which is crucial in high-risk zones. In airport control rooms or service areas where equipment may emit significant heat, lead glass serves a dual purpose—protecting against radiation and ensuring safety in extreme thermal conditions.
- Modern technologies – lead glass in protective windows with adjustable transparency
In response to the growing need for radiation protection in various conditions, lead glass is increasingly used in combination with innovative adjustable transparency technology. Protective lead glass windows with adjustable transparency allow for tailoring the level of protection based on changing radiation intensity. For instance, in baggage scanning zones, where radiation levels may vary depending on the scanner’s settings, this adjustable transparency can enhance protection in the most exposed areas.
- Lead glass combined with other protective materials
Lead glass is often combined with other protective materials to enhance its effectiveness and durability. For example, in protective cabins where operators monitor baggage scanning processes, lead glass is frequently paired with metal protective panels or composites. This combination makes the protection system more resistant to mechanical damage while ensuring effective radiation shielding.
Practical applications of lead glass at airports
At airports, where security control is a priority, lead glass has a wide range of applications. Specifically, lead glass is used in:
- Protective cabins for X-ray scanner operators.
- Protective windows in baggage scanning rooms.
- Protective glazing in security control areas.
- Protective partitions in laboratories.
Thanks to lead glass, airport staff can safely monitor the scanning and inspection processes of baggage without being exposed to X-ray radiation. Lead glass windows in these areas provide effective radiological protection while maintaining full transparency for the staff.
Summary
Lead glass is an essential material for providing protection against radiation at airports, where baggage inspection relies on devices emitting X-ray radiation. With its effectiveness in blocking radiation, transparency, heat resistance, and innovative technological solutions, lead glass is widely used in various airport zones, ensuring the safety of both staff and passengers.
These features make lead glass one of the most important materials used in airports, where X-ray radiation is an integral part of baggage control procedures. Lead glass enables convenient, safe, and efficient work in control zones and other areas where radiation may pose a threat. Additionally, innovative solutions such as adjustable transparency and combinations with other protective materials make lead glass increasingly adapted to modern radiological protection needs.
If you want to learn more about the applications of lead glass and other protective materials at airports, visit Coradika.pl, where you will find a wide range of radiation protection products.